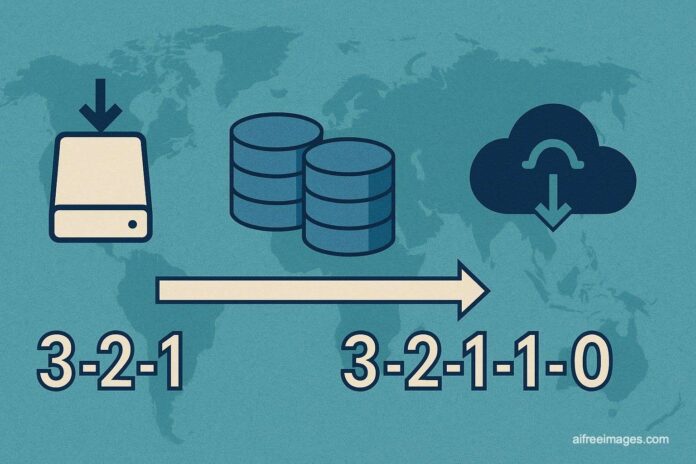
In the modern business context, where data is the heart of organizations, backups have gone from being an optional recommendation to an essential requirement. The traditional 3-2-1 rule, although useful at the time, is being renewed to face contemporary threats with the 3-2-1-1-0 strategy.
This advanced approach contemplates five basic pillars: maintaining three copies of critical data, storing them on two types of media, ensuring at least one copy off-site, another offline or air-gapped, and guaranteeing zero errors through regular testing. This approach is a response to a threat landscape in which threats have become more sophisticated, especially in the realm of ransomware, and where factors such as human errors and supplier failures also play a critical role.
Currently, cyberattacks have evolved, targeting not only production data but also backups. Organizations face risks that are not only technological, but also derived from administrative errors and vendor failures, as evidenced by a landmark case in 2023 where an AWS customer lost a decade's worth of data due to failures in the internal protocols of the technology company.
In economic terms, the average cost of a data breach rose to 4.88 million dollars in 2024, a stark reminder that not having a robust backup strategy can be fatal. The 3-2-1-1-0 rule offers a way to mitigate these risks through a technical implementation that spans strategically distributed copies, media diversification, and the always-crucial integrity verification.
Recent cases underscore the importance of this strategy. An incident at Microsoft Azure and another at Google Cloud highlighted how even the largest tech companies can face significant outages, confirming that geographic diversification and provider diversification is an essential step.
The 3-2-1-1-0 rule is also framed within a context of technological innovation, with immutable backups and artificial intelligence emerging as allies to anticipate failures and improve preventive actions. Additionally, with the expansion of edge computing, backup strategies must be adapted to ensure that crucial data in multiple locations are managed and adequately protected.
The benefit of applying this methodology is reflected not only in the protection of assets, but also in the competitive advantage that guarantees operational continuity and customer confidence. The digital era demands a proactive and sophisticated approach to data management, placing the 3-2-1-1-0 rule as a fundamental piece in any modern business strategy to strengthen its resilience and secure its future in an increasingly interconnected economy.
More information and references in Cloud News.